The Definitive Barcode Inventory Management Guide
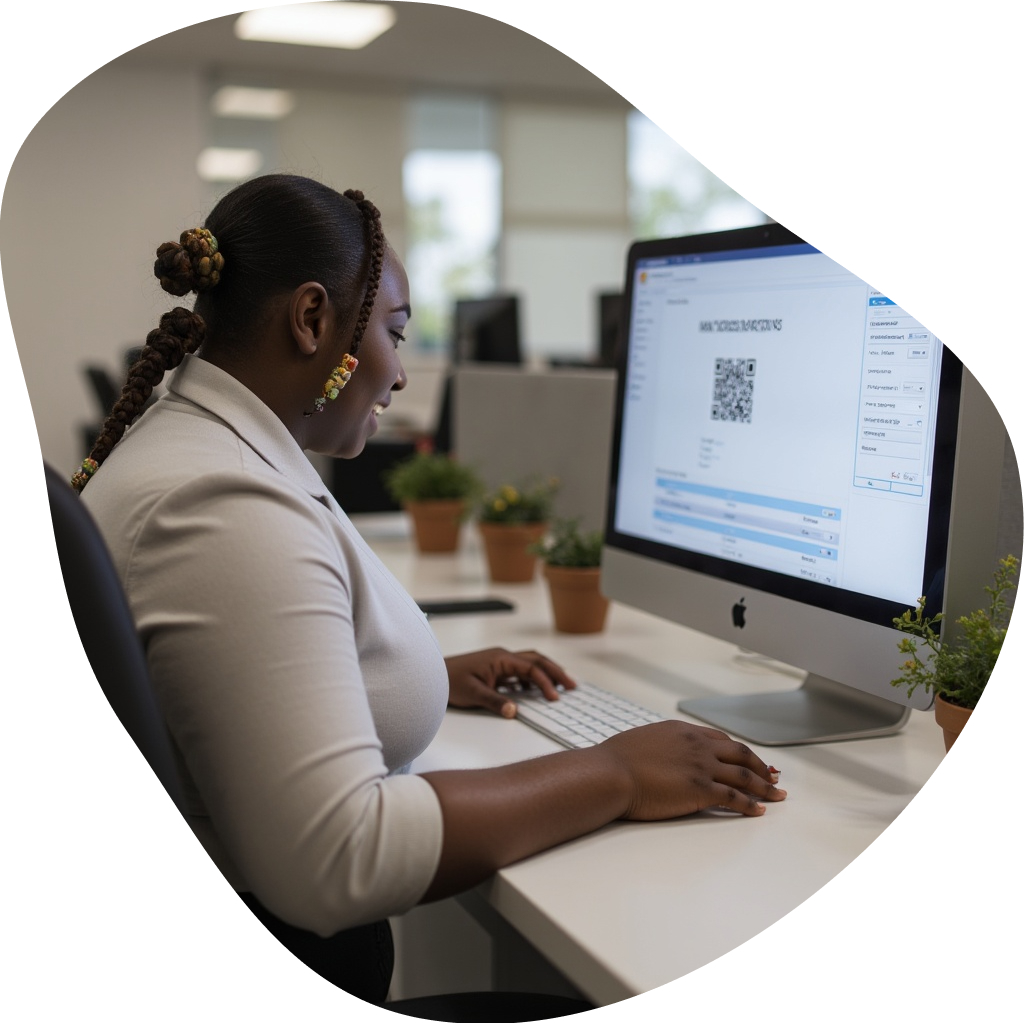


Transforming Warehouses with Modern Barcode Inventory Management
In today's competitive business landscape, warehouses face tight margins and rising customer expectations—manual logs simply can't keep pace.
Barcode inventory management replaces error-prone spreadsheets with real-time scanning technology, dramatically reducing mistakes while boosting operational speed.
This guide will equip you with:
- Essential components of effective barcoding systems
- Data-backed benefits that impact your bottom line
- Step-by-step implementation roadmap
- Smart criteria for selecting the right solution
For small and medium businesses, this technology delivers enterprise-level control without the complexity or cost that typically accompanies such systems.
See the bigger picture with our comprehensive barcode inventory system overview to understand how these technologies work together.
Defining Barcode Inventory Management for SMB Warehouses
Barcode inventory management is a digital method that pairs scannable labels with cloud software to track every stock movement in your warehouse. Unlike manual inventory counting—where staff physically count items and update spreadsheets—a barcode inventory management system automatically captures data when items are scanned, eliminating human counting errors and spreadsheet drift that plague paper-based systems.
For small and medium businesses with teams of 2-50 people, inventory accuracy directly impacts your bottom line. When your barcoding inventory management system shows you have 15 units but only 12 exist, you face costly consequences:
- Customer frustration from oversold products
- Wasted staff time searching for phantom inventory
- Rush shipping costs to fulfill unexpected shortages
- Increased return processing from shipping errors
Barcode Types at a Glance
Most SMB warehouses use one of two barcode formats:
-
1D (Linear) Barcodes: The familiar parallel lines you see on retail products. These store limited information like SKU or UPC codes and work well for basic inventory tracking.
-
2D Barcodes: More advanced patterns (like QR codes) that hold significantly more data including batch numbers, expiration dates, and serial numbers in a smaller space.
Your choice between these types depends on what information you need to track and your scanning equipment capabilities. For a deeper understanding of which barcode type best suits your operation, our barcode types guide provides a comprehensive comparison.
With a proper barcode system, warehouse staff spend less time counting and more time serving customers—turning inventory management from a liability into a competitive advantage.
The Building Blocks: Labels, Scanners, Software
A complete barcode inventory system requires three fundamental components working together to deliver accuracy and efficiency. Understanding these elements helps businesses select the right configuration for their unique operations.
Labels & Media
High-quality barcode labels are the foundation of any effective inventory system. These labels must withstand your specific environment – resisting moisture in cold storage, heat in manufacturing facilities, or frequent handling in retail settings. Selecting the right adhesive and material ensures your labels remain scannable throughout your product lifecycle, preventing costly rescanning or manual entry. For more details on label options, visit our barcode labels guide.
Scanners
The right scanning hardware dramatically impacts workflow efficiency. Options range from traditional handheld devices to wearable scanners that free up both hands for picking. For smaller operations, smartphone-based scanning apps offer an affordable entry point, though dedicated scanners provide better durability. Your choice should align with daily scanning volume and environmental conditions. Explore our guide to selecting the ideal barcode scanner for inventory.
Software
Inventory management software with barcode scanner capabilities transforms raw scanned data into actionable business intelligence. Cloud-based solutions offer advantages for distributed teams, while on-premises systems may better serve businesses with limited connectivity. The software should facilitate multi-user synchronization to prevent conflicting inventory counts.
Integration capabilities are crucial – your system should connect with point-of-sale systems, shipping platforms, and accounting software. For businesses just starting, an automatic barcode generator simplifies creating standardized codes.
From Receiving to Shipping: How a Barcode Inventory Management System Fits Every Workflow
A comprehensive barcode inventory management system transforms operations across your supply chain by creating a seamless flow of information from arrival to shipment. Here's how this technology powers each critical stage:
1. Receiving & Put-Away
Employees scan incoming products to instantly create receipt records, validate quantities against purchase orders, and update inventory counts. The system guides workers to optimal storage locations, reducing put-away time significantly.
2. Location Transfers
Moving inventory becomes error-proof with an inventory management system with barcode scanner functionality. Workers scan the item, scan the destination, and the system records the movement in real-time, preventing "lost" inventory.
3. Cycle Counts
Rather than disruptive full inventory counts, barcode systems enable targeted cycle counting on a rotating schedule, making verification faster while maintaining accuracy.
4. Picking & Order Processing
When orders arrive, the system creates efficient picking paths, directing staff through the warehouse. Barcode verification ensures the right items are picked every time, streamlining order picking operations.
5. Packing & Shipping
During packing, final scans confirm order completeness before generating shipping labels. Mobile capabilities allow work during network outages, and the intuitive interface means new hires become productive quickly.
Proven Benefits: Data-Backed ROI of Adopting Inventory Management Software With Barcode Scanner
Implementing a barcode inventory system delivers measurable returns that justify the initial investment. Organizations consistently report significant operational improvements after transitioning from manual processes:
Measurable Performance Improvements
- Error Reduction: Businesses experience up to 67% fewer inventory mistakes when using an inventory management system with barcode scanner compared to manual entry methods
- Efficiency Gains: Picking speed increases by approximately 30%, allowing the same staff to handle greater order volume
- Inventory Accuracy: System users achieve 99% inventory visibility accuracy, virtually eliminating costly stockouts and overstock situations
These statistics directly address common operational pain points. Human error during manual inventory counts costs businesses an average of 4-6 hours per week in reconciliation time. The search time for misplaced inventory drops dramatically, with workers spending up to 75% less time hunting for products.
For comprehensive financial analysis, our barcode inventory system roi calculator helps businesses project their specific returns based on current operational metrics.
When compared to manual systems, an inventory management system with barcoding provides the infrastructure to scale operations without proportional increases in labor costs. As your business grows, the system accommodates higher transaction volumes with minimal additional investment.
The initial investment varies based on implementation scale and existing infrastructure. For a detailed breakdown of potential expenses, see our barcode system cost analysis that covers hardware, software, and barcode labels considerations.
Unlike manual processes that become increasingly unwieldy with growth, barcode systems demonstrate greater ROI as transaction volume increases, making them particularly valuable for growing businesses.
Five-Stage Implementation Roadmap (With Pitfalls to Avoid)
Implementing a successful barcode inventory management system requires careful planning and execution. Follow this proven five-stage approach to ensure your transition happens smoothly:
1. Assess & Map Current Processes
Begin by documenting your existing inventory workflows. Identify pain points, bottlenecks, and manual steps that consume excessive time. This baseline assessment provides critical metrics to measure your improvement after implementation.
2. Prepare Data and Generate Labels
Clean your inventory database before generating barcodes. Remove duplicate SKUs, standardize naming conventions, and verify quantities. This foundational step is crucial—even the most advanced system will fail with poor data quality. Learn more about proper setup in our how to set up a barcode inventory system guide.
3. Hardware & Software Pilot
Test your selected solution in a controlled environment before full deployment. Choose a small product category or warehouse section to verify scanner accuracy, software integration, and workflow improvements. This reveals technical issues while limiting disruption.
4. Staff Training and Phased Rollout
Develop role-specific training materials and schedule hands-on sessions. Implement the system in phases, department by department, allowing staff to gain confidence while maintaining operations. Consider designating "power users" who can assist colleagues.
5. Optimization & Reporting
After implementation, continuously refine your processes based on performance data. Configure dashboards to track key metrics like inventory accuracy, picking speed, and order fulfillment times.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid:
- Dirty or damaged barcode labels causing scan failures
- Inadequate Wi-Fi coverage in warehouse areas
- Skipping data cleanup before implementation
- Insufficient training for temporary or seasonal staff
Remember that successful barcode inventory management requires clean item masters and consistent processes. Small issues can compound quickly, so address them immediately during implementation.
For businesses considering implementation options, our barcode inventory system for small business guide provides tailored recommendations to fit your operation scale and budget.
Troubleshooting & Maintenance
Maintaining a well-functioning barcode inventory system requires vigilance and proactive management. Even the best systems encounter issues, but knowing how to address them quickly minimizes disruption to your operations.
Typical issues
Barcode misreads and duplicate codes frequently undermine inventory accuracy, creating reliability problems in your data.
Damaged labels from moisture, abrasion, or temperature extremes make products invisible to your tracking system.
Scanner connectivity problems stem from weak WiFi signals or Bluetooth failures, creating operational bottlenecks.
Data sync lags create discrepancies between your inventory database and physical stock availability.
Preventive actions
Regular inventory audits identify discrepancies before they impact operations. Implementing systematic label reprint cycles ensures deteriorating barcodes are replaced proactively.
Keeping scanner firmware updated prevents compatibility issues and improves read rates. Many barcode scanner for inventory problems resolve with simple updates.
Periodic network assessments identify dead zones affecting barcode tracking system performance, especially in warehouse environments.
For comprehensive maintenance strategies and additional troubleshooting guidance, our common barcode problems and fixes guide provides detailed solutions for long-term system reliability.
Mini Case Study Carousel: E-commerce, Manufacturing, Retail
E-commerce Success Story
An independent seller struggled with inventory discrepancies when transferring products to Amazon FBA warehouses. After implementing a mobile barcode scanning solution, they reduced transfer errors by 80% within three months. The key lesson: even simple barcode systems can deliver significant improvements when deployed at critical transfer points in your operation.
Manufacturing Transformation
A small manufacturer with three production facilities faced challenges tracking lot numbers across their operation. By implementing a barcode inventory management system that connected all locations, they gained complete visibility into material movements. This allowed them to trace components from receipt through production to finished goods, reducing recall scope by 94% during a quality incident.
Retail Revival
A boutique clothing retailer was overwhelmed during holiday seasons, with staff spending excessive time on inventory counts. After introducing batch scanning with a barcode scanner for inventory, they doubled their checkout throughput while maintaining accuracy. Their insight: start with scanning in one department to build confidence before expanding storewide.
Each success story demonstrates how even modest investments in barcode tracking systems can deliver quantifiable returns for businesses of different sizes and sectors. The common thread across all cases: starting with clear problem identification before selecting technology led to more successful implementations.
Smart Selection Guide: Evaluating an Inventory Management System With Barcoding for Your Business
Choosing the right inventory management system with barcoding requires careful assessment of your specific business needs. A system that revolutionizes one operation might create bottlenecks in another.
Evaluation criteria
Feature alignment should be your starting point. Determine whether you need lot tracking, multi-location capability, or offline scanning functionality. Manufacturing operations typically require lot tracking, while retail prioritizes multi-location support.
System flexibility matters. Some solutions offer templated setups with limited customization, while others provide greater configurability at the cost of more complex implementation.
Integration breadth determines how seamlessly your barcode inventory system connects with existing technology. Look for native connections to shipping platforms, accounting software, and e-commerce channels to eliminate double-entry.
Consider the total cost of ownership beyond initial price. Factor in hardware, implementation, training, and support. The barcode system cost varies widely based on these factors.
Vendor support quality can make or break your implementation. Evaluate their onboarding process and training resources. Small businesses should consult our barcode inventory system for small business guide for specific considerations.
Before finalizing, benchmark potential solutions against your requirements, using our main barcode inventory management overview for technical specifications.
Why Finale Inventory Delivers Exceptional Barcode Inventory Management Results
Finale Inventory's barcode inventory system stands out for businesses implementing their first warehouse management solution, offering a powerful yet accessible platform that addresses common pain points without requiring enterprise-level budgets.
Tailored to first-time WMS adopters
Finale Inventory provides highly configurable workflows designed specifically for growing businesses transitioning from manual processes to automated systems. The platform includes wave picking, pick-and-pack, and batch picking options that can be customized to your warehouse layout.
"Using the scanner's 'guided picking' feature, order picking is a breeze and easy for old and new employees to understand as the scanner determines the most efficient picking order and guides them to the correct standard bin where each product is located. The Finale team is always very helpful and understanding whenever I have issues." – Sharon, Operations Manager @ Ontario Beer Kegs
The mobile scanner functionality works offline when WiFi connections are unreliable and can "learn" new barcodes dynamically by simply scanning them and associating them with your inventory items.
Human-error elimination
The barcode inventory management solution verifies every item during picking, receiving, and transfers, dramatically reducing costly mistakes that lead to returns. The system excels at handling complex scenarios including Amazon FBA transfers, serial numbers, and lot ID tracking.
"I used to do stock takes with pen and paper. Using Finale and a mobile barcode scanner I get it done in half the time. Last Saturday I never would have finished doing stock takes for my 60 sublocations without the scanner and Finale. A must have for any small business looking to save time with inventory management." – Robert Fenton, Operation Manager @ Miami Restaurant Supplies
Rapid, affordable deployment
Unlike million-dollar ERP add-ons that require lengthy implementation cycles, Finale offers an off-the-shelf SaaS solution backed by white-glove onboarding services. This approach delivers enterprise-level functionality at a price point accessible to small and mid-sized businesses.
Integration capabilities include flexible APIs, CSV imports/exports, and FTP options that connect with your existing systems.
Scalable hardware choices
The barcode inventory system works with various hardware options to fit your budget and operational style:
- Android-integrated barcode scanners for comprehensive warehouse management
- Smartphone scanning capabilities for cost-conscious operations
- Bluetooth ring scanners for high-volume picking environments
This flexibility ensures your investment remains valuable as your business grows.
Compliance & traceability
For businesses requiring detailed traceability, Finale excels at handling multi-part lot IDs, serial numbers, and GS1 barcode parsing. The system automatically unpacks information from heterogeneous barcode types, eliminating manual data entry.
"The software provides a simple solution to a common problem managing a single inventory through multi platform online sales channels – eBay, Amazon, and webstore – using Finale. It's easy to use for staff, smooth integration to Shipstation, easy integration with online platforms with more APIs in the works, and great tech support. Handheld scanner enables staff to add and remove inventory with ease." – Chiman Lee, Director of Recompute @ Goodwill Industries of San Francisco, San Mateo, and Marin counties
See how a barcode inventory system can transform your warehouse operations by scheduling a demo or starting a free trial today. For businesses considering different approaches, explore barcode inventory system alternatives to understand all available options.
Conclusion
Barcode inventory management represents the modern backbone of efficient warehouses, blending accurate data capture, adaptable software, and streamlined workflows to empower business growth with precise inventory control.
We've explored the essential components: specialized labels, reliable scanners, and intelligent software that ties everything together. The ROI is clear and measurable – reduced errors, lower labor costs, fewer stockouts, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced operational efficiency.
Successful implementation follows a staged approach from planning to continuous improvement. When selecting the right system, consider your unique business requirements, growth trajectory, and integration needs.
Adopting an inventory management system with barcode scanner positions your business to handle growth efficiently while minimizing costly errors that plague manual systems. This technology gives businesses of all sizes competitive advantages in their operations.
Ready to transform your warehouse? Explore our complete barcode inventory system guide or contact Finale Inventory to start improving your warehouse today.
Frequently Asked Questions
Barcode inventory management is a system that uses barcodes to track and monitor inventory items throughout their lifecycle. Instead of manually recording inventory data, employees scan barcodes with specialized devices or smartphones to instantly update inventory records. This digital approach creates real-time visibility into stock levels, locations, and movements. For businesses managing warehouses, a barcode inventory management system drastically reduces human error, increases operational efficiency, and provides accurate data for better decision-making. It forms the backbone of modern warehouse operations by connecting physical items to digital records.
The best barcode type depends on your specific business needs. For basic inventory tracking, traditional 1D barcodes (UPC, EAN, Code 128) work well and are widely compatible with most scanners. For businesses needing to store more information in limited space, 2D barcodes like QR codes and Data Matrix are superior options. Businesses tracking lot numbers or serial numbers often benefit from GS1-128 barcodes which follow standardized formats for product information. The optimal choice balances information density requirements, scanning equipment capabilities, and integration with your barcode inventory system. Consider future needs—many businesses start with 1D codes but migrate to 2D as operations grow.
Barcode inventory system costs vary widely based on complexity and scale. Basic smartphone-based solutions start around $50-100/month for small businesses. Mid-range systems with dedicated hardware typically cost $3,000-10,000 for initial setup (including scanners, software licenses, and labels) plus ongoing subscription fees of $100-500 monthly. Enterprise-grade warehouse management systems with advanced barcode capabilities can exceed $25,000+ for implementation. When calculating total cost, consider hardware (scanners, printers), software subscriptions, implementation services, training, and ongoing support. Many businesses see barcode inventory system ROI within 6-12 months through reduced errors and improved efficiency.
Barcodes serve as the crucial link between physical inventory and digital records in modern warehouse management. They enable instant identification of products, locations, and order information through simple scans. This capability transforms labor-intensive processes like receiving, putaway, cycle counting, and order picking into streamlined, error-resistant workflows. Barcodes eliminate manual data entry errors (typically reducing mistakes by 80-95%), accelerate operations, and enable real-time inventory visibility. They also facilitate advanced capabilities like lot tracking, serial number management, and expiration date monitoring. For growing businesses, barcodes provide the foundation for scaling warehouse operations while maintaining accuracy and efficiency.
Creating a barcode inventory system involves five key steps. First, assess your business needs and select appropriate barcode inventory management software that integrates with your existing systems. Second, decide on barcode types (1D or 2D) and generate unique identifiers for your products and locations. Third, purchase necessary hardware including barcode scanner for inventory and printers. Fourth, set up your physical warehouse with labeled locations and configure your software with inventory data. Finally, train your team on new scanning procedures and workflows. Most businesses benefit from working with an implementation specialist who can tailor the system to specific requirements and provide best practices for your industry. The complete how to set up a barcode inventory system typically takes 2-8 weeks.
SKUs (Stock Keeping Units) and UPCs (Universal Product Codes) serve different purposes in barcode inventory management. SKUs are internal identifiers created by your business to track product variations like size, color, or style. They're customizable and optimized for your operations. UPCs are standardized 12-digit codes registered with GS1 that uniquely identify products across all retailers globally. While SKUs help organize inventory within your business, UPCs facilitate external communication with suppliers, retailers, and point-of-sale systems. Most barcode inventory systems use both: SKUs for internal operations and UPCs for purchasing, sales, and integration with other systems. Sophisticated systems can automatically map between these identifiers for seamless inventory tracking.
A barcode inventory system works by connecting physical items to digital records through scanning. When inventory arrives, warehouse staff scan product barcodes to log quantities and details in the system. The software assigns storage locations, which staff confirm by scanning location barcodes during putaway. For order fulfillment, the system generates pick lists, and workers scan items to verify accuracy before shipping. Throughout these processes, each scan updates inventory counts in real-time. The system maintains comprehensive records of all movements, providing visibility into stock levels, item history, and performance metrics. Modern systems often integrate with accounting, e-commerce, and shipping platforms to create a unified business ecosystem with barcodes at its foundation.
Several barcode types are commonly used for inventory management, each with specific advantages. UPC and EAN codes are standard for retail products, while Code 128 offers flexibility for alphanumeric data. For advanced needs, GS1-128 barcodes can encode batch numbers, expiration dates, and weights within a single code. QR codes and Data Matrix (2D barcodes) are gaining popularity as they store significantly more information in less space, supporting detailed product data and tracking information. Many businesses use multiple barcode types simultaneously: location labels might use simple Code 39, while products use UPC for retail compatibility and QR codes for internal tracking of complex information. The right choice depends on your information needs and scanning environment.
Inventory tracking is the foundation of operational efficiency and financial health for product-based businesses. Without accurate tracking, companies face costly challenges including stockouts (leading to lost sales and customer dissatisfaction), overstocking (tying up capital and warehouse space), and inventory shrinkage (from theft, damage, or administrative errors). Proper inventory tracking ensures optimal stock levels, reduces carrying costs, and enables data-driven purchasing decisions. It also supports customer satisfaction through accurate delivery promises and timely fulfillment. For businesses with regulated products or quality control requirements, tracking lot numbers and expiration dates becomes essential for compliance and safety. As businesses grow, robust inventory tracking becomes increasingly critical to maintaining profitability and operational control.
For items without manufacturer barcodes, you can create and print custom barcode labels using your inventory management software and a thermal label printer. First, add the item to your system with a unique SKU and product details. Next, use the software's label printing function to generate barcodes (typically Code 128 or QR formats work well). Print these on adhesive labels and apply them to the products or their storage containers. For bulk items or materials sold by weight, consider creating barcode labels for standard quantities or for the storage location instead of individual items. This approach allows you to maintain consistent scanning workflows for all inventory, regardless of whether items arrived with manufacturer barcodes or not.
Calculating total inventory value requires multiple valuation methods depending on your business needs. The simplest approach multiplies each item's quantity by its cost (acquisition price plus inbound shipping, taxes, etc.). For financial reporting, businesses typically use one of three methods: FIFO (First-In-First-Out), LIFO (Last-In-First-Out), or weighted average cost. A comprehensive barcode inventory management system automatically tracks these calculations based on your chosen method. Beyond basic valuation, sophisticated systems can highlight metrics like slow-moving inventory value, projected inventory costs based on sales forecasts, and carrying costs. These insights help businesses optimize working capital and make informed purchasing decisions that balance stock availability against capital efficiency.
Yes, modern barcode inventory management systems provide automated low stock alerts through multiple channels including email, SMS, mobile notifications, and dashboard indicators. These systems allow you to set minimum threshold levels for each product based on factors like sales velocity, lead times, and seasonality. When inventory drops below these thresholds, the system triggers notifications to appropriate team members. Advanced systems offer dynamic reorder points that automatically adjust based on sales patterns and can even generate purchase orders for approval. This automation ensures you maintain optimal inventory levels without constant manual monitoring, preventing both stockouts and overstock situations that impact your bottom line.
Yes, smartphones can function as barcode scanners using inventory management apps with built-in scanning capabilities. This approach provides flexibility and cost advantages for small businesses or companies with occasional scanning needs. Most modern smartphones have cameras capable of reading both 1D and 2D barcodes with reasonable speed and accuracy. However, dedicated barcode scanners offer significant advantages for higher-volume operations: they scan 3-5 times faster, include rugged designs for warehouse environments, offer superior battery life, and provide ergonomic features to reduce operator fatigue. Many businesses start with smartphone scanning and graduate to dedicated devices as volume increases. Some implement hybrid approaches using smartphones for cycle counts and dedicated scanners for high-velocity picking operations.
Implementation timeframes for barcode inventory systems typically range from 2 weeks for basic setups to 3+ months for complex enterprise deployments. Small businesses using cloud-based systems with minimal customization can often be operational within 2-4 weeks, including software configuration, barcode generation, and basic training. Mid-sized operations requiring integration with existing systems, custom workflows, and comprehensive staff training usually need 6-10 weeks. The implementation process includes several phases: planning and system selection, software configuration, hardware setup, warehouse organization and labeling, data migration, integration testing, staff training, and a monitored launch period. Working with experienced implementation specialists significantly reduces timeframes and ensures best practices are followed from the start.
The most common implementation challenges include resistance to change from warehouse staff, integration issues with existing business systems, data migration complexities, and hardware selection mistakes. Change management requires clear communication about benefits and comprehensive training to overcome staff resistance. System integration challenges can be mitigated through proper planning and leveraging inventory systems with robust API capabilities. Data quality issues often surface during migration—products with duplicate SKUs, inconsistent naming conventions, or inaccurate counts. Hardware selection mistakes typically involve choosing equipment that doesn't match workflow needs or environmental conditions. Successful implementations address these challenges through thorough planning, staged rollouts, and common barcode problems and fixes that might arise during the transition.
Barcode inventory management dramatically improves picking accuracy by implementing verification checkpoints throughout the fulfillment process. When pickers scan each item and location during picking, the system instantly validates that the correct product, quantity, and location match the order requirements. This verification prevents common errors like picking similar-looking items, wrong quantities, or items from incorrect locations. Advanced systems support various picking methodologies including wave picking, batch picking, and zone picking with barcode verification at each step. The result is typically a reduction in picking errors from industry averages of 1-3% down to 0.1-0.5%. This improvement directly translates to fewer returns, higher customer satisfaction, and reduced labor costs associated with correcting mistakes and processing returns.
1D barcodes (like UPC, Code 128) consist of parallel lines and spaces that encode limited data—typically 8-25 characters. They're widely used, work with most scanners, print reliably on various materials, and scan quickly from a distance. However, they require more physical space per character stored. 2D barcodes (QR codes, Data Matrix) encode information both horizontally and vertically, storing significantly more data (hundreds to thousands of characters) in the same space. They can contain complete product specifications, maintenance records, or URLs to digital resources. 2D codes also offer superior error correction, allowing successful scans even when partially damaged. While traditional 1D codes remain sufficient for basic inventory tracking, businesses needing to encode lot numbers, serial numbers, or detailed product information increasingly migrate toward 2D solutions.
Modern barcode inventory management systems offer multiple integration methods with accounting and e-commerce platforms. These typically include direct API connections, middleware solutions, CSV imports/exports, and pre-built integrations with popular platforms like QuickBooks, Shopify, and Amazon. These integrations synchronize critical data including inventory quantities, orders, product information, and financial transactions. When inventory is received or shipped using barcode scanning, the system automatically updates connected platforms to maintain accurate stock levels across all sales channels. This synchronization prevents overselling, ensures accurate financial reporting, and eliminates manual data entry. The best solutions provide real-time or near-real-time updates, although some businesses opt for scheduled synchronization intervals based on their operational requirements and transaction volumes.
Seamless Barcode Integration
Set up your inventory for long-term growth with barcoding automation

Get Started with Finale
Free implementation during your free Finale trial. No long-term contracts; you'll be on the path to scaled business growth in just two weeks.
Get a demo on the
first call.Pricing is fair and
transparent.Onboarding starts
during your free trial.
Get a demo on the
first call.Pricing is fair and
transparent.Onboarding starts
during your free trial.
Your time is valuable. That's why we jump into the software during your first call.
Finale offers competitive pricing because users stay and grow.
Free implementation during your trial so you can see Finale in action.